Azure DNS is used for two scenarios:
- Internet-facing name resolution for a public DNS Domain.
- Internal name resolution, e.g., Virtual machines within VNets.
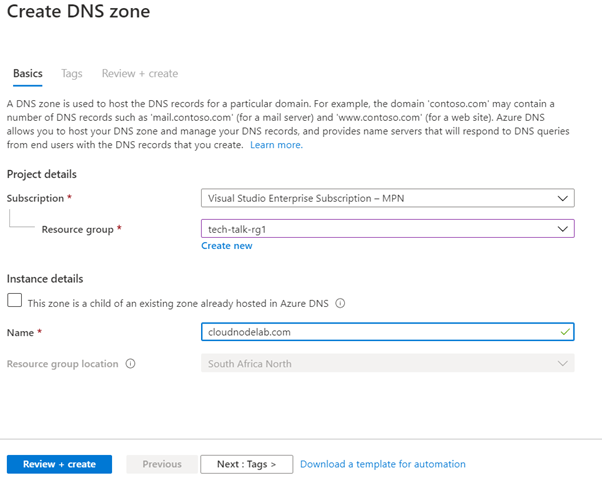
To get started creating DNS Zones, login to Azure and search for DNS Zone.
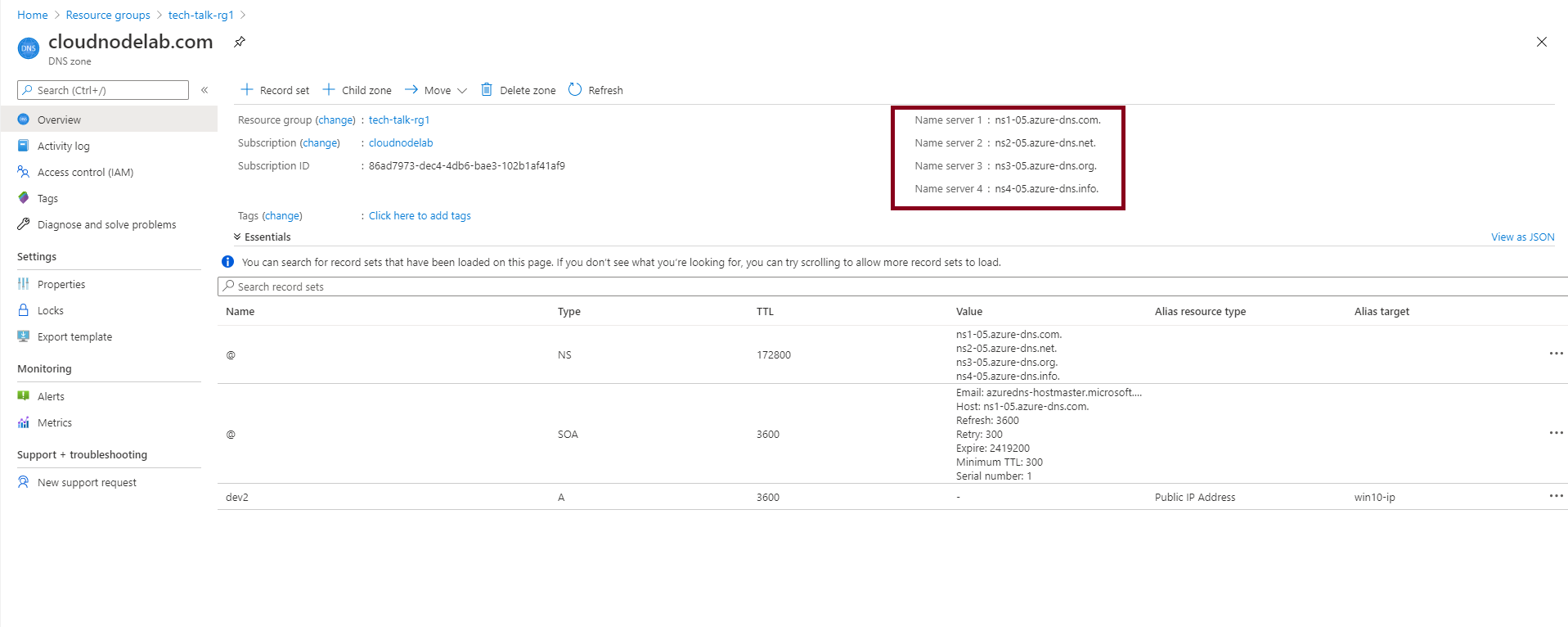
When it's done creating, the Name servers assigned to our zone are shown below.
Private DNS Zones
Private DNS Zones are used to isolate your network interfaces/Azure virtual networks and the associated resources, for example, virtual machines from the Azure provided DNS Public service.
Next, create a DNS Private Zone.
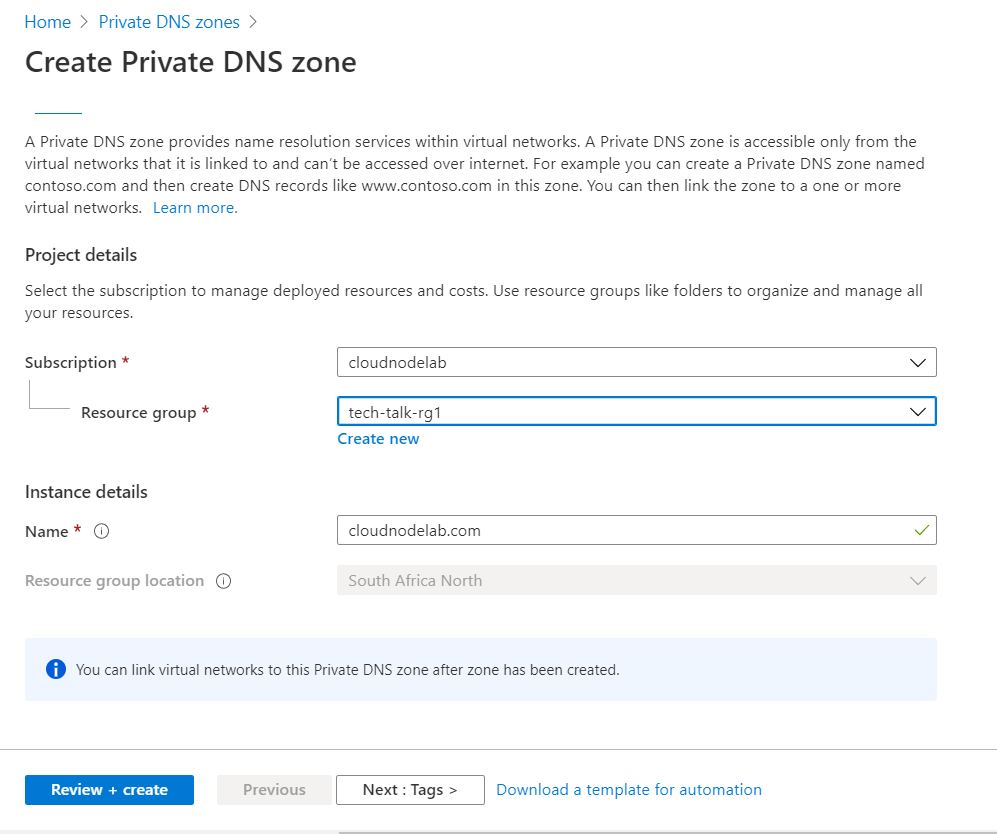
When it's done creating, you will get something similar to what we created in the Public DNS Zone, only that this time we have an SOA record only and a private DNS host.
To join our resources to this new zone, we shall register the vNets on which our resources are found, and then this will enable them to get the private IP addresses from the private zone.
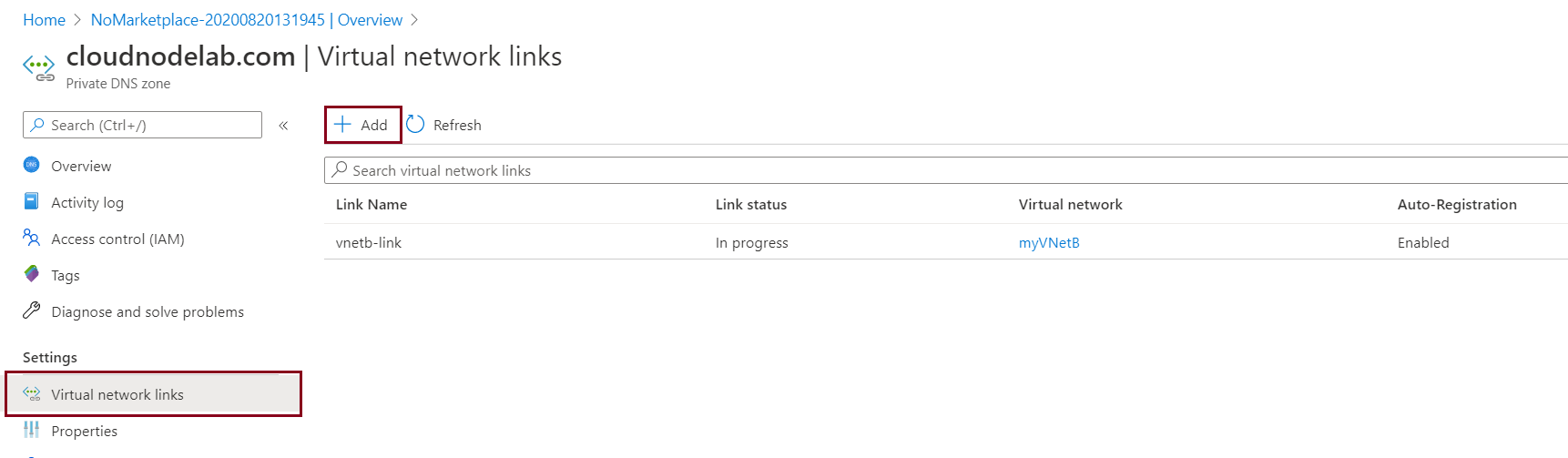
To effect the changes, I will restart one of my virtual machines and it will add a DNS record to the private zone automatically.
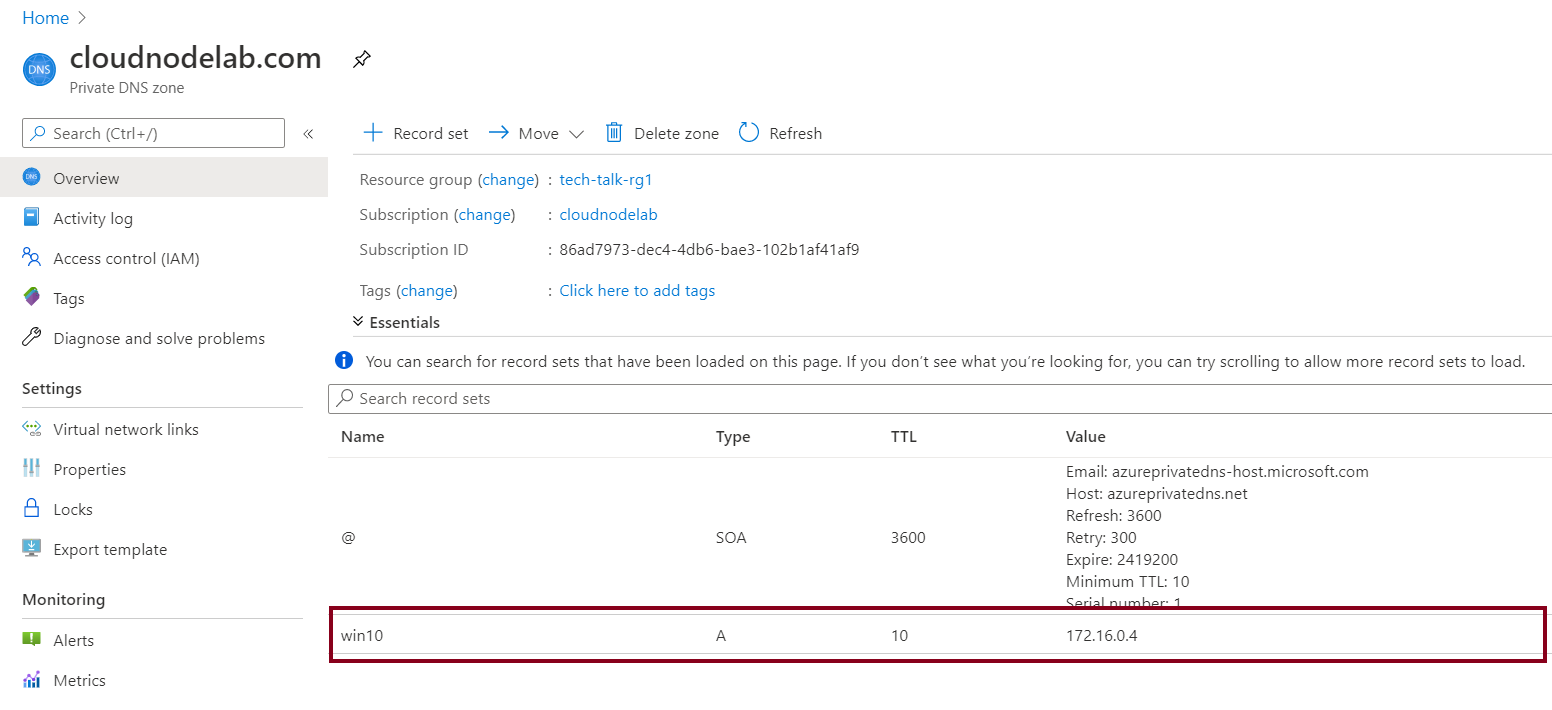
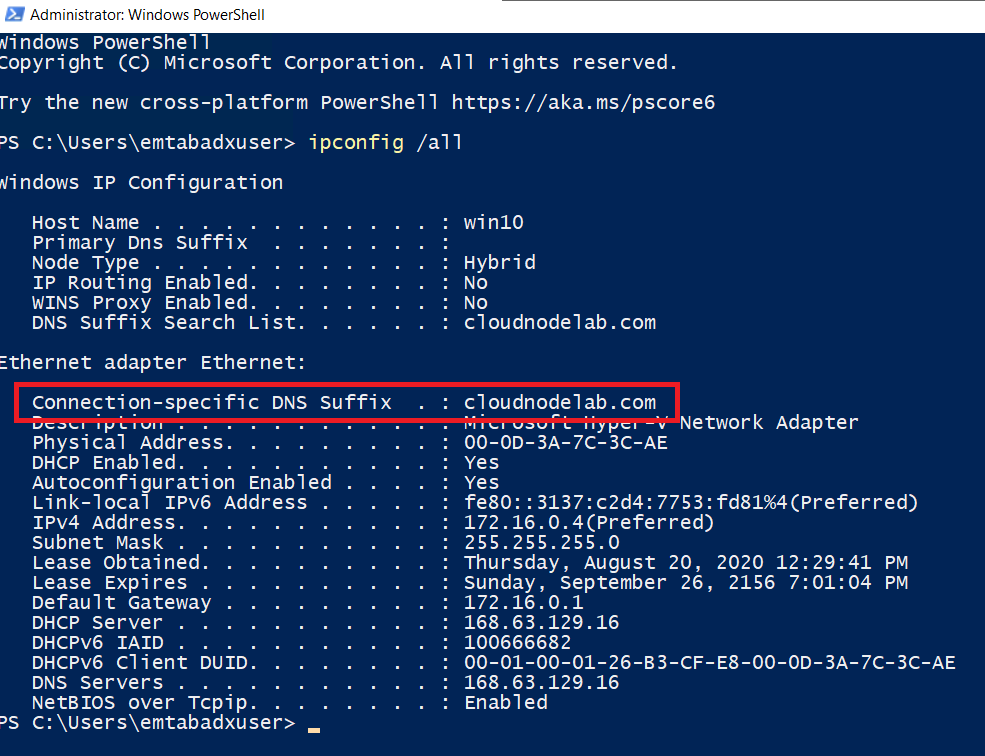
To configure your VM to use the new DNS suffix, you can do it manually on the machine, or you can also do it on multiple machines using a Powershell script.
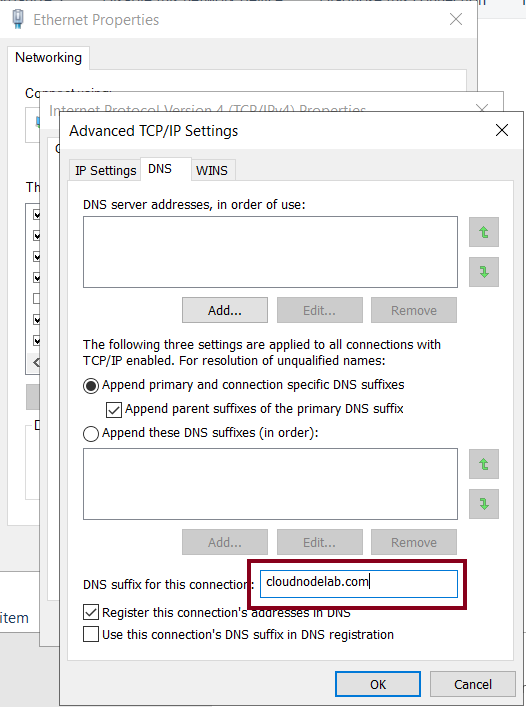
After restarting the machine, you will be able to see the DNS Suffix of the private DNS zone.